What Is Eco-Gardening?
Eco-gardening is a collection of environmentally friendly practices for cultivating plants and maintaining gardens and lawns with minimum environmental impact. The goal is to choose plants that create a harmonious and balanced ecosystem without synthetic chemicals and with consideration for how you use natural resources.

Eco-gardening follows natural growing cycles and relies exclusively on biological processes. As you get started with sustainable gardening, you learn to respect “nature’s ways,” which will encourage the presence of beneficial insects, protect the ecosystem from invasive species, and minimize water loss. This approach will create a balanced ecosystem where plants flourish and wildlife thrive. And, if you also use your garden to grow food, an ecosystem that produces nutrient-rich herbs, fruits, and vegetables.
Why Is Eco-Gardening Important?
Sustainable gardening practices like composting and mulching contribute to water conservation and climate change mitigation. These practices play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, as the organic matter in compost and mulch traps carbon in the soil, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere. Plus, emphasizing natural growing cycles and pesticide-free practices improves your land’s health in the long run.
Because all living organisms within a garden are connected, gardening in line with natural patterns promotes resilience and balance. In the bigger picture, eco-gardening is critical for preserving biodiversity. Cultivating varied native plant species supports a range of animal life, including beneficial insects and pollinators.
Beyond environmental benefits, sustainable gardening positively impacts personal well-being and community dynamics. Individuals engaged in eco-gardening experience physical and mental health benefits, while community gardens encourage shared responsibility for individual and collective well-being.
Pros of Growing a Sustainable Garden
- Balanced ecosystems
- Biodiversity enhancement
- Improved soil structure and fertility
- Water conservation
- Access to healthier food
- Active support for pollinators like bees and butterflies
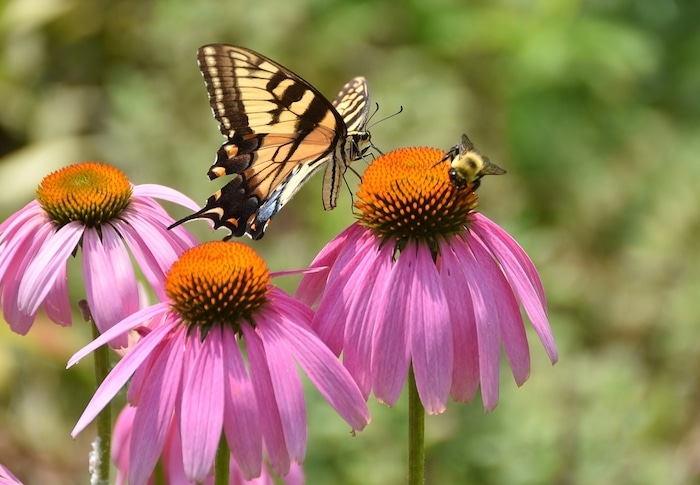

- Carbon sequestration
Eco-Gardening for Beginners: 5 Ways to Create An Eco Garden
- Keep The Soil Healthy
Fertile land is the foundation of a sustainable garden. You want to continuously infuse organic matter to keep the soil’s structural integrity. At the same time, you provide a nurturing environment for millions of microscopic life forms that maintain your garden healthy for longer periods.
What to focus on:
- Shield the ground from harmful chemicals that could disrupt essential microbiological activity, like pesticides or synthetic fertilizers.
- Use compost and mulch to build a robust defense mechanism. Composting introduces valuable nutrients and encourages the proliferation of beneficial microbes. On the other hand, a protective layer of mulch acts as a natural shield against erosion, temperature extremes, and moisture loss, promoting overall resilience.

- Sustain a nutrient-rich habitat with crop rotation and cover cropping. Crop rotation ensures a diverse range of plants with varying nutrient needs, preventing soil depletion and enhancing its fertility over time. Cover crops and grass fortify the ground by shielding it during periods of dormancy, adding organic material, and preventing nutrient leaching.
- Garden Sustainably with Rainwater
Rainwater harvesting is a powerful strategy for water conservation and sustainable gardening practices. Rainwater will reduce dependence on municipal water systems and wells and prevent runoff. From an environmental perspective, relying on rainwater lessens the energy and infrastructure required for water treatment and distribution — further reducing the carbon footprint associated with water consumption.
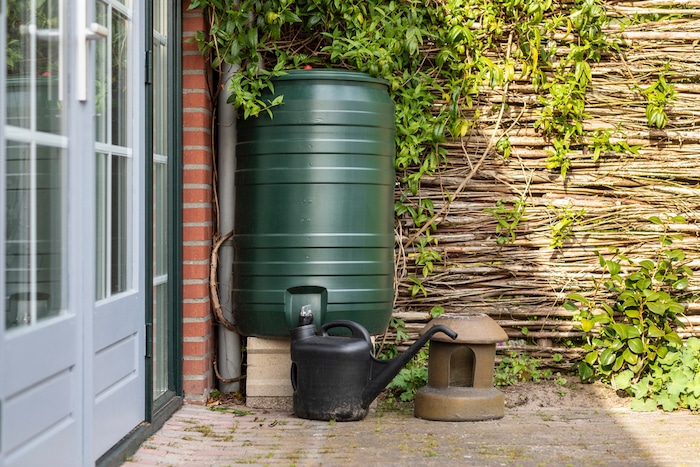

What to focus on:
- Build an efficient rainwater harvesting system. It should include gutters to collect rain from the roof, downspouts to channel water into storage containers, and a filtration mechanism to remove debris.
- Optimize the storage capacity of your collection system to meet your garden’s needs. It would be best to have a reliable supply during dry periods to use supplemental irrigation as little as possible.
- Match rainwater collection efforts with a sustainable irrigation method for maximum efficiency. For example, drip irrigation or soaker hoses can deliver rainwater directly to plant roots, minimizing water wastage through evaporation and runoff.
- Plant Native Plants for Diversity
Diverse eco-gardening plants contribute to a balanced and dynamic habitat, attracting beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. Beyond the aesthetic appeal, a diverse garden is better equipped to withstand pests, plant diseases, and environmental challenges.
What to focus on:
- Choose grass and plants that vary in size, form, and flowering times. The diversity creates a visually engaging garden and provides different niches for various organisms.
- Prioritize native plant species adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. They support regional biodiversity and often require less maintenance, contributing to the overall sustainability of your lawn or garden.
- Create a planting plan incorporating a mix of annuals, perennials, and shrubs, paying attention to their blooming periods to ensure year-round interest. Introduce companion plants strategically, considering factors like pest resistance and nutrient-sharing capabilities.
- Grow Only As Much As You Can Manage
It’s about having a garden of sufficient size to guarantee its ongoing health, proper maintenance, and enjoyment, all without a sense of overwhelming responsibility. This approach also preserves resources, helps with time management, and minimizes potential environmental issues associated with neglect.
What to focus on:
- Assess the available space and resources, considering sunlight, soil health, and water availability. Choose grass and plants that can flourish in your garden without excessive intervention.
- Consider your time commitment and prioritize low-maintenance plants or those that require minimal attention.
- Plant a curated selection of species that complement each other and contribute to a harmonious landscape. This strategy simplifies maintenance and enhances the overall aesthetic value of the garden.
- Save Seeds for Sustainable Gardening
This age-old tradition preserves and propagates plant varieties adapted to local conditions over time. Beyond the immediate benefits of cost savings and a continuous supply of seeds, this practice contributes significantly to environmental conservation and fostering resilient, regionally adapted ecosystems.
What to focus on:
- Plant open-pollinated or heirloom plant varieties as they generally produce seeds that stay true to the characteristics of the parent plant. It maintains genetic diversity and preserves the unique qualities of each species.
- Allow seeds to mature on the plant before collection, and then dry and store them in a cool, dry place.
- Label and organize your seed collection meticulously. Accurate record-keeping ensures that you can trace the origin and characteristics of each seed batch for successful future plantings.
BONUS: 5 Eco Gardening Ideas
- Start with a low-maintenance garden. Plant native and drought-resistant eco-gardening plants, prioritizing perennials over annuals for long-term sustainability. Apply a thick layer of mulch to suppress weeds and build an automated irrigation system. Establish a routine maintenance schedule for pruning and occasional weeding so the garden remains visually appealing with minimal effort.
- Build a compost pile. Homemade compost is a natural fertilizer that enhances your land’s fertility with a well-balanced mix of essential nutrients. Moreover, the organic matter in compost improves soil aeration, water retention, and drainage, creating an optimal environment for plant roots. Plus, composting serves as a means of waste reduction and recycling, diverting organic materials such as kitchen scraps and yard trimmings from landfills.
- Use garden beds. They enhance soil fertility, structure, and drainage while simplifying monitoring and adjusting pH levels. The method is excellent for water conservation and weed suppression. In cooler climates, elevated beds will absorb and retain heat more effectively, allowing for earlier planting in the spring and later harvesting in the fall.
- Enrich your eco-garden with fruits and vegetables. Plan your garden layout using companion planting principles to enhance growth, deter plant pests, and create a healthier ecosystem within the garden. Encourage natural predators like ladybugs and beneficial insects to control pests. Planting companion herbs like basil or marigolds can also help protect your vegetables.
- Plant one or more trees in your eco garden. Trees sequester carbon, mitigate climate change, and provide habitats for diverse wildlife. Their shade regulates temperatures, conserving water and fostering a stable microclimate. Planting trees is also an investment for the future — a fully grown tree will absorb approximately 22 kilograms of carbon dioxide yearly.
Eco-Gardening Examples for Beginners
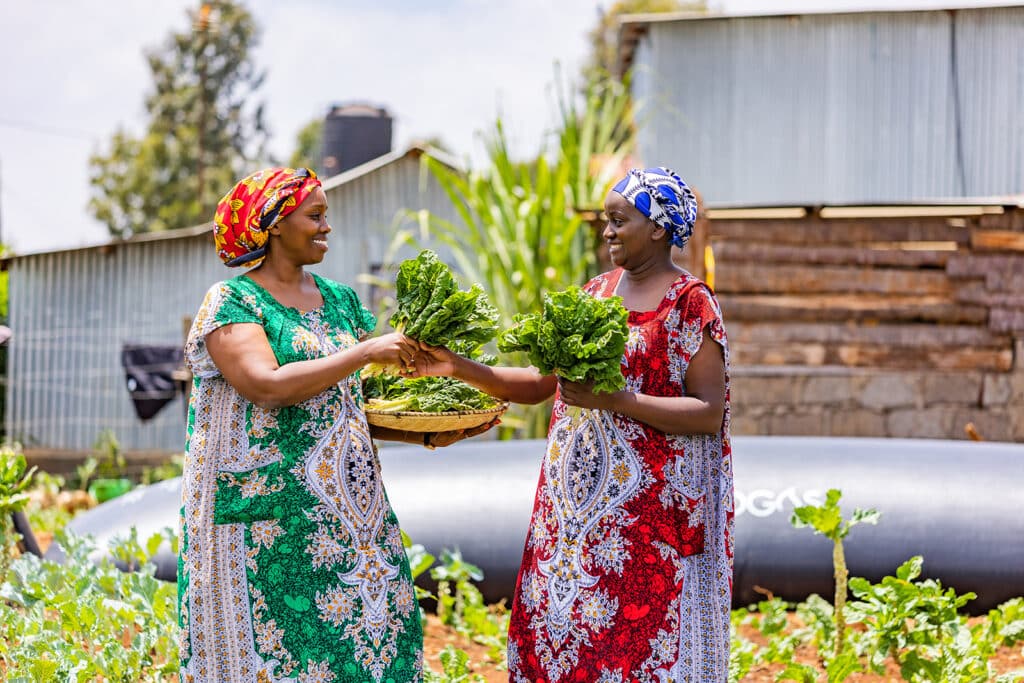
Rachel has a passion for cultivating fresh, flavorful produce with sustainable methods. She appreciates the incomparable taste of a freshly picked juicy peach, a crisp apple, a sweet strawberry, or a vine-ripened tomato, far surpassing what supermarkets sell. By integrating eco-friendly practices into her Australian eco-garden, Rachel has established a sustainable and fulfilling ecosystem that provides her family with healthy food. Her commitment extends to recycling organic matter—utilizing animal manure, kitchen scraps, and garden waste to produce 100% organic fertilizer, boosting the health of her plants with environmentally conscious methods.
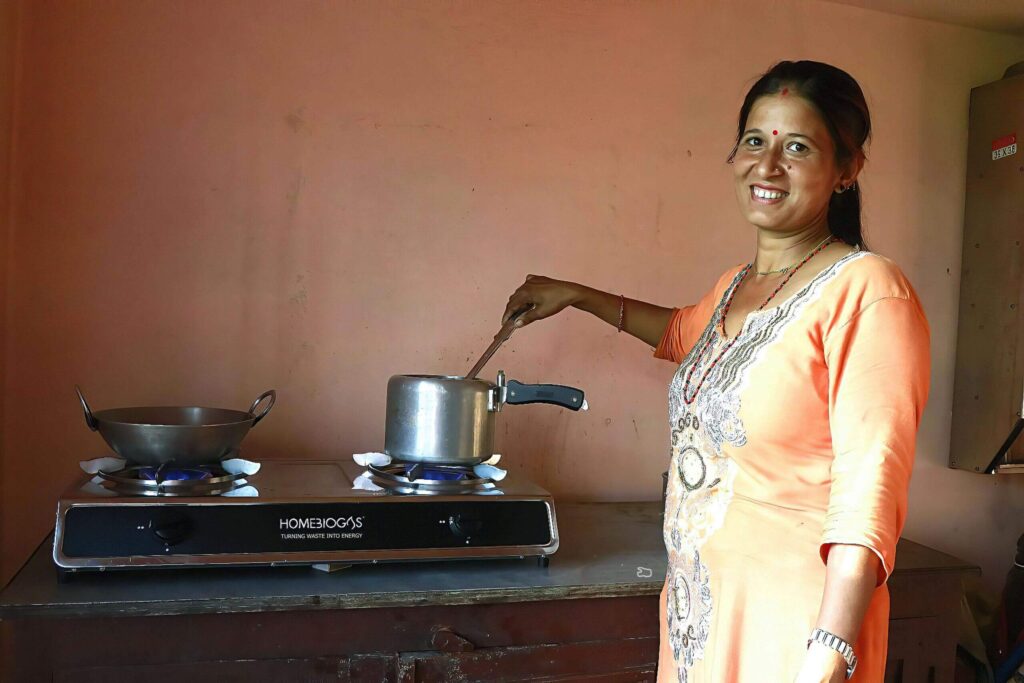
In Atlanta, Georgia, Kemble is dedicated to keeping a thriving eco-garden. He uses homemade fertilizer, so the vegetables he grows for his family are all-natural and organic. Taking his commitment to sustainability further, Kemble has built a biogas system to maximize the potential of organic waste from the garden. This innovative approach creates a circular domestic economy model, emphasizing self-sufficiency and reducing environmental impact by harnessing organic waste for energy.
Meet HomeBiogas – Turn Your Organic Waste into Clean, Renewable Cooking Gas & Rich Fertilizer
HomeBiogas systems transform organic waste, typically directed to landfills, into valuable resources: biogas for cooking and organic bio-fertilizer.
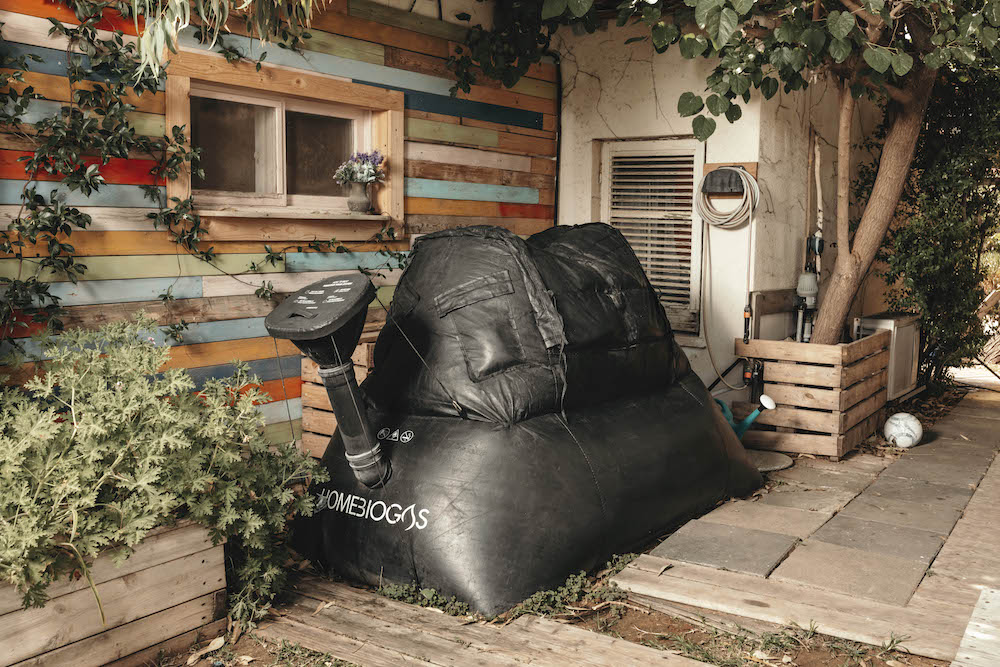

The system uses a biodigester that captures and processes organic waste to produce biogas. It also incorporates a gas storage system for collecting and storing the generated biogas, ensuring a reliable and continuous supply for household use. The kit comes with a gas stove for cooking purposes and all the necessary accessories, such as pipes and connections, to facilitate seamless integration into your home.
How a HomeBiogas system can support your eco-friendly garden design:
- Waste reduction and waste-to-energy conversion: you can convert all the organic waste from your garden (with your kitchen waste and other organic materials) into biogas through anaerobic digestion.
- Fertilizer production: besides biogas, anaerobic digestion also produces a nutrient-rich fertilizer known as digestate. This liquid is an excellent source of essential plant nutrients, replacing synthetic fertilizers and promoting healthier plant growth.
HomeBiogas can support your broader efforts to adopt a sustainable lifestyle by addressing key facets of environmental responsibility. Plus, using biogas for cooking and water heating reduces reliance on non-renewable energy sources, aligning with other global initiatives to transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
Final Thoughts
Transitioning from traditional gardening to eco-friendly practices may require a shift in mindset and habits, but the long-term benefits are worth the initial effort. Beyond the tangible advantages of a thriving garden, embracing eco-gardening becomes a fulfilling journey. The aesthetic appeal of your lawn or garden and the quality of your crops won’t be compromised; instead, they are enhanced through a sustainable approach that respects natural processes.
You create an environment that nurtures plants, fruits, and vegetables in harmony with nature through clever planning, organic fertilization, and companion planting. This nature-centered approach ensures the health of your garden and supports a diverse and resilient ecosystem, supporting beneficial insects and local wildlife for a healthy ecosystem.





