The Goals of An Effective Kitchen Waste Disposal System
Effective kitchen waste disposal is more than taking out trash every evening. It’s a mindset and lifestyle shift toward a thoughtful and responsible way of dealing with kitchen garbage so your actions have minimal environmental impact.
As part of this process, you need to change your habits and meet four primary goals:
- Produce less kitchen waste.
- Sort everything before it heads to the landfill.
- Compost and recycle.
- Send trash to the right destination.
Eco-friendly kitchen waste disposal habits give results when the entire family joins the challenge. Everyone must participate daily so your household produces less trash overall and contributes to a cleaner environment.
Types of Kitchen Waste
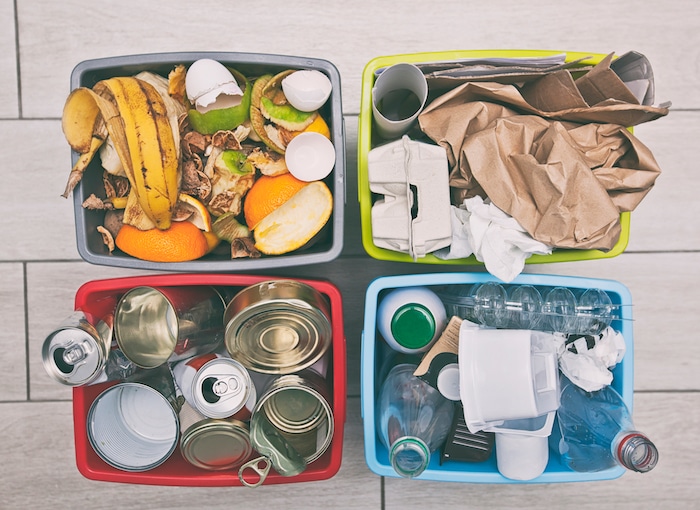
Getting familiar with the various types of kitchen waste helps with the fourth goal — finding the appropriate bin for everything you throw away from your kitchen. Here’s what you need to know:
Organic Kitchen Waste:
- Fruit and vegetable peels and cores, bread, eggshells, plate scrapings, coffee grounds, and tea bags
- Leftover, spoiled, or expired food
- Paper towels and napkins that came into contact with food
- Plant trimmings and dead leaves from your kitchen garden
- Bones, skin, and trimmings from meat and fish
- Spoiled milk, cheese rinds, and yogurt containers
Inorganic Kitchen Waste:
- Plastic wrappers, containers, and packaging materials from grocery products
- Disposable utensils, plates, and cups
- Empty cans
- Empty glass jars and bottles
- Broken or worn-out pots, pans, utensils, and kitchen appliances
- Non-recyclable materials, like rubber bands, broken glass, and heavily soiled or non-recyclable paper.
- Cleaning products and their packaging
Proper Sorting and Disposal Techniques
Sorting rules usually follow local regulations, as they’re aligned with the waste management solutions available in your area. As a rule of thumb, you’ll have to separate food scraps from non-recyclable items, so only recommended products end up in recycling facilities. The more attention you pay, the easier it becomes to process waste at later stages.
Composting is the ideal disposal technique for organic materials. So, separate all leftovers and expired foods and use them to participate in community composting efforts when possible. Alternatively, you can install a composting system in your backyard or purchase a kitchen composting bin with a lid to produce compost at home.
For other recyclables, you want to sort them into paper (newspapers, cardboard), glass (bottles, jars), plastics (bottles, containers), and metals (aluminum cans). Local recycling guidelines will give you specific instructions for disposing. Generally, you’ll have to rinse containers to remove any residue, clear labels, and place recyclables in designated recycling bins or bags.
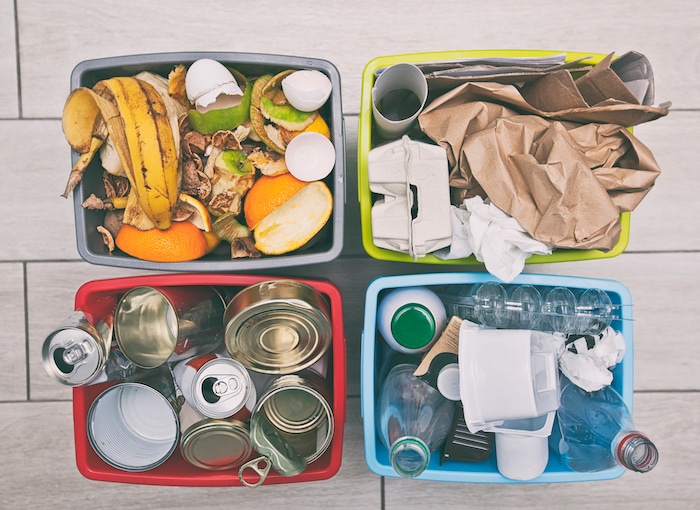

Non-recyclables like plastic bags, disposable diapers, and broken glass must go into the regular trash bin.
Educating and Engaging Your Household
Now that you know what needs to be done and how to do it, it’s time to coordinate efforts among family members so they all do their part. The workload is distributed if everyone is actively involved, and the process becomes more manageable.
So, how do you engage everyone? It’s best if you make the learning process enjoyable. Watch short educational videos together, and then challenge family members to categorize items as recyclable, compostable, or trash correctly. You can also try a rewards system or incentives to make it more exciting.
Creating easily accessible recycling stations within your home will also help. Label bins or containers clearly for different waste streams and encourage everyone to use them. You can also involve the family in meal planning and grocery shopping, teaching them to buy only what’s needed to reduce food waste.
The secret is to start with achievable waste reduction goals and only commit to tasks that can quickly become part of your daily routines. This way, everyone can keep up and follow your lead towards a greener lifestyle.
The Three Rs: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Kitchen waste disposal is easier when you adopt the “Three Rs” concept — Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. Follow these guidelines, and you’ll see how trash in your house shrinks. These principles will also teach you and your family how to build responsible consumption and waste-reduction practices.
- Reduce. It’s about making conscious choices to consume fewer resources and products. Buy fewer disposable items, and you’ll have less trash in your kitchen bins.
- Reuse. Instead of discarding products after a single use, find creative ways to repurpose or repair them. Think shopping bags, containers, and kitchen appliances. Reusing items saves you money and reduces the need for new manufacturing.
- Recycle. Divert as many materials from landfills as possible — paper, cardboard, glass, metal, plastic, grease, and batteries from kitchen gadgets.

These three Rs work together to promote responsible resource management and waste reduction. They encourage a shift from a linear “take-make-dispose” economy to a more sustainable one.
Benefits of Effective Kitchen Waste Disposal
- Fewer non-recyclable items end up in landfills. This, in turn, minimizes the production of harmful greenhouse gases and supports better usage of resources.
- Food scraps and organic materials get a second life as compost, a nutrient-rich soil amendment that enhances soil health and provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
- You cut down costs for your households and the municipality. Waste management costs get smaller with less stuff to collect, transport, and process.
- You keep your kitchen clean and sanitized. Proper kitchen waste disposal prevents the accumulation of spoiled food and reduces the risk of contamination, foodborne illnesses, and foul odors.
- You conserve resources like water and energy because you become more aware of the environmental impact of your daily choices.
5 Effective Strategies for Kitchen Waste Disposal
1) The Easiest to Implement: Composting as a Sustainable Solution
Composting is one of the most straightforward and eco-friendly ways to manage kitchen waste. It involves collecting and decomposing organic materials like food scraps and coffee grounds to create nutrient-rich compost.
This method is effective because it reduces the amount of waste, enriches soil quality, and promotes plant growth. It’s easy to start by setting up a small compost bin in your kitchen or backyard.
2) Easy to Implement: Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste is another simple but highly effective strategy to manage garbage disposal. It involves improving shopping habits, mindful meal planning, and using leftovers creatively.
Buying only what you need helps you save money and minimize the environmental impact of food production and waste management.
3) Moderately Easy to Implement: Recycling
Most communities have recycling programs that make the process relatively easy. Find out what kitchen waste is suitable for recycling in your area, and start collecting them separately.
The difficulty is ensuring that all recyclable materials are in the right place and don’t accidentally mix with regular trash. When non-recyclable materials enter the recycling stream, they can disrupt operations at recycling facilities and diminish the quality of recycled products, so pay attention to local guidelines.
4) Moderately Complex: Waste-to-Energy
Some communities have waste-to-energy facilities that can convert non-recyclable items into renewable energy. These plants divert thousands of tons of waste from landfills and produce green energy for their communities.
It’s a more complex strategy as it requires specific infrastructure and technology.
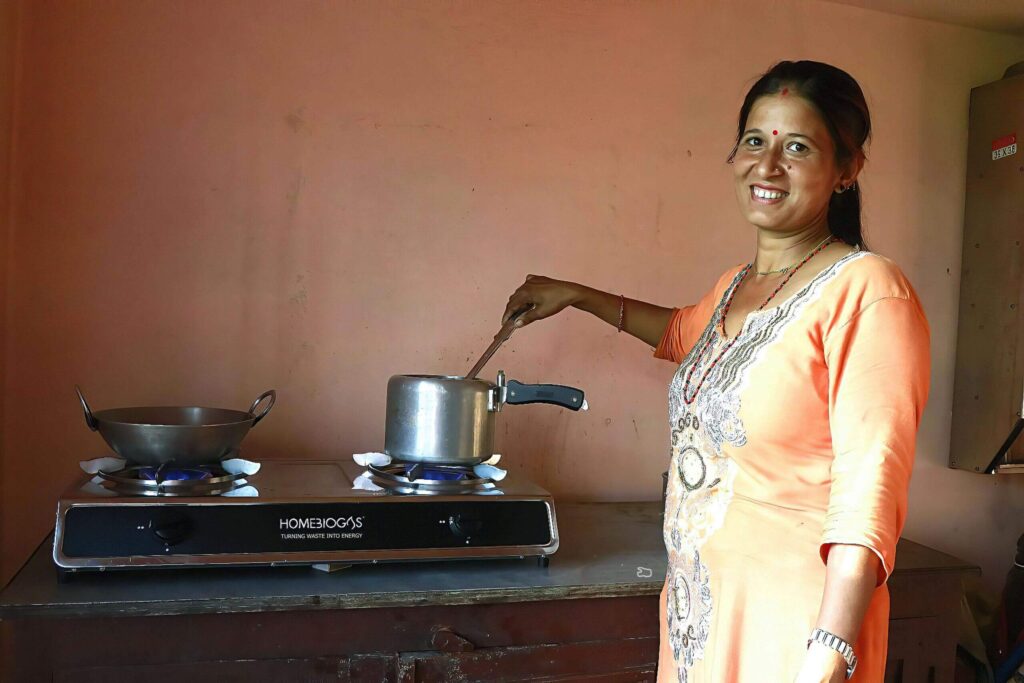
5) Moderately Complex: Turning Kitchen Waste into Biogas at Home
HomeBiogas systems can convert organic kitchen waste into biogas for cooking or heating. The process involves setting up a biogas digester, which can be more complex than composting in your backyard.
It also requires an investment in equipment and maintenance but can be a sustainable and rewarding solution for kitchen waste disposal and energy generation.
Innovative Kitchen Waste Disposal Methods
Here are some more cutting-edge devices that use technology to address the challenges of kitchen waste management and environmental sustainability.
- Food waste digesters. They break down organic kitchen waste into compost or liquid effluent within hours. Depending on their complexity, some digesters can even handle items like meat, bones, and dairy products. Digesters produce compost for sustainable gardening practices.
- Smart bins with sensors. They use artificial intelligence (AI) technology to streamline waste collection and management. These bins can sort waste automatically and notify you when they reach capacity to prevent overflowing bins.
- Zero-waste kitchen design. It incorporates built-in compost bins, food scrap collection systems, and integrated recycling stations to make kitchen waste separation and disposal effortless and intuitive.
- Anaerobic digestion facilities. They use anaerobic bacteria to break down organic matter (food, wastewater, and human waste) and capture biogas. These large-scale facilities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and create a more sustainable energy mix.
Meet HomeBiogas — Your Solution for Turning Waste into Biogas
HomeBiogas solutions solve kitchen waste disposal challenges with an easy and innovative approach. Using user-friendly biodigesters, homeowners can transform organic matter into biogas in their backyard.
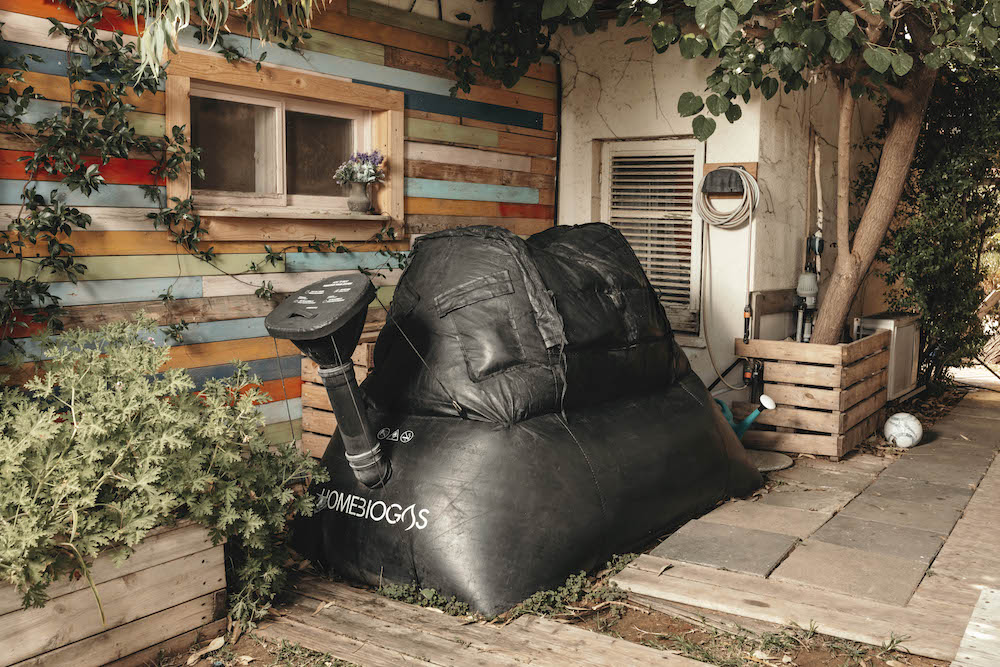

HomeBiogas systems operate on the principle of anaerobic digestion — microorganisms break down organic materials like food scraps and animal waste in an oxygen-free biodigester, yielding biogas and Bio-fertilizer as a byproduct.
All systems are designed for easy installation and usage, making them accessible to homeowners, farmers, and businesses. The kit includes the biodigester, a dedicated stove, and all the pipes and tools necessary to set up and maintain the system. Homeowners need a designated outdoor area and organic waste materials, such as food scraps and animal waste, readily available in most households. The system operates automatically once set up, requiring minimal maintenance.
The residual output of HomeBiogas is a nutrient-rich liquid Bio-fertilizer that enhances soil quality in gardens. It’s an innovative solution that simplifies kitchen waste disposal for a more sustainable future.
What’s Next?
Proper kitchen waste disposal is a practical and achievable goal that benefits you and the planet. If you want to get started today, here are some actionable steps:
- Learn about local waste disposal guidelines, recycling programs, and composting options. This way, you’ll know what to recycle and what you can compost.
- Start meal planning, reduce portion sizes, and use leftovers to minimize food loss.
- Create designated bins or containers for different waste streams in your kitchen so everyone can sort waste correctly.
- If you have the time and space, start composting your kitchen scraps in a backyard compost bin or consider investing in innovative solutions like HomeBiogas for biogas production.
Start small and gradually incorporate these practices into your daily routine. Over time, you’ll find that proper kitchen waste disposal becomes a natural part of your lifestyle, with a long-term impact on your household and the environment.