Why Turning Waste into Energy Matters
Converting municipal solid waste into energy through anaerobic digestion or waste-to-energy incineration can prevent debris buildup in landfills and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Landfills, often seen as the necessary evil in municipal waste management, can have disastrous environmental consequences. They disrupt the natural landscape and emit around 570 million tonnes of methane annually, contributing significantly to climate change. Furthermore, rainwater percolating through landfills can become contaminated with harmful chemicals, leading to soil and water pollution.

Plus, waste incineration in outdated facilities can release toxic substances and heavy metals into the atmosphere.
On the other hand, waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies aim to minimize emissions and capture pollutants to prevent harmful substances from reaching the atmosphere.
Moreover, waste as a renewable energy source can reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy production, paving the way for a greener energy future.
Waste-to-Energy Examples
- Waste-to-energy incineration. Non-recyclable waste materials are burned at high temperatures to produce electricity. This solution is gradually becoming obsolete as new waste management trends prioritize reducing waste generation. Ongoing efforts to reduce single-use plastics and encourage responsible consumption aim to lead to a decline in the volume of waste suitable for incineration. Instead, waste management systems lean toward more energy-efficient and eco-friendly solutions, such as advanced recycling technologies that enable resource recovery.
- Anaerobic digestion. This process involves waste decomposition without oxygen to produce biogas and digestate. The biogas is used for generating electricity or as a renewable natural gas source. Biogas production has seen disparate growth worldwide, depending on the availability of feedstocks and supportive policies. Europe, China, and the United States collectively constitute 90% of global biogas production. In China, household-scale digesters have been promoted in rural areas, while the United States focuses on landfill gas collection and agricultural waste for biogas. With growing interest globally, the biogas industry is expected to expand further, with countries like Thailand and India also making notable contributions.

- Gasification. The process is one of the most effective methods for recovering energy from biomass, primarily by producing syngas, a carbon monoxide and hydrogen mixture. The syngas can help generate electricity, heating, biofuels, and chemicals, but the number of large-scale gasification plants globally is low. Most of these plants are in European countries and Japan, mainly because they lack landfill space. In developing countries, gasification is limited due to challenges like different types of waste, varying waste sizes, high moisture content, and less efficient gasifier and gas cleaning systems.
- Pyrolysis. Pyrolysis involves heating solid waste in the absence of oxygen. Through this process, plastics primarily produce oil, while wood and woody biomass yield syngas and char as their main products. Pyrolysis is more eco-friendly than traditional incineration because it emits fewer toxic pollutants. Additionally, pyrolysis plants generate less noise pollution than standard incineration facilities.
Pre-treatment and Preparation of Waste
Pre-treatment involves mechanical sorting to separate municipal waste fractions and reduce oversized items into manageable pieces. At this stage, hazardous substances and potential equipment-damaging items are eliminated from the waste stream. Recyclable recovery is essential for extracting valuable materials like plastics, metals, and paper.
Pre-treatment can also include preprocessing organic waste for WTE facilities that produce green energy through anaerobic digestion.
As an individual, you can actively contribute to pre-treatment success by:
- Properly sorting and separating your waste at home.
- Removing non-recyclable (expanded polystyrene, plastic bags, dirty paper, ceramics, disposable diapers) and hazardous waste (batteries, electronics, pesticides, medicine, solvents) from your waste.
- Participating in community recycling programs to divert recyclable materials.
- Turning food waste into energy at home through composting or domestic biogas production.
7 Best Practices for Turning Waste into Energy
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. The foundation of waste-to-energy starts with personal waste reduction efforts. Prioritize reducing consumption, reusing items, and recycling materials whenever possible.
- Sort your waste. Proper sorting at home enhances the quality of waste that is used for energy conversion, improving the overall efficiency of the process.
- Buy responsibly. Opt for items with minimal packaging or those made from recyclable materials. Supporting products with eco-friendly packaging minimizes the negative impact of your waste.
- Educate yourself. Learn about the WTE technologies available in your area to understand their benefits, environmental impacts, and safety measures.
- Support renewable power sources. Promote and use, when possible, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Reducing reliance on fossil fuels contributes to the broader goal of transitioning to cleaner alternatives.
- Compost at home. Composting food scraps and yard trimmings diverts these materials from landfills and produces nutrient-rich compost that can enhance soil health. Can you turn waste into energy at home? Yes. If you want to take this further, you can manage organic waste with anaerobic digestion to generate biogas for cooking and biofertilizer for your lawn or garden.
- Build energy-efficient habits. Practices like using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when not needed, and conserving water support waste-to-energy efforts.
Research and Development in Waste-to-Energy Technology
The academic community are actively engaged in extensive research on various technologies for waste disposal.
Research and development consider geographical, temporal, and technological factors when selecting the most suitable technologies and facility locations. Other factors considered are the chemical composition of waste, addressing uncertainties, and environmental impacts.
Research also aims to integrate waste-to-energy technology within broader energy systems. Smart grid integration, energy storage solutions, and grid-balancing strategies are under investigation to ensure the seamless integration of waste-derived energy into existing infrastructure.
Overcoming Challenges and Mitigating Risks
Waste-to-energy technology demands rigorous tests and improvement before adoption at scale to ensure efficiency and safety. Moreover, integrating these technologies into existing waste management infrastructure can pose further compatibility and scalability challenges.
These technologies must remain monitored to prevent unintended consequences, such as air and water pollution, especially when regulatory frameworks lack clarity. Navigating these technological challenges and risks demands a delicate balance between innovation, safety, and environmental responsibility.
The process is time-consuming and resource-intensive, so local and global commitment is necessary. International cooperation frameworks can provide the financial support and technology transfer mechanisms necessary for sustainable waste management at scale. Also, robust government policies and regulations are needed to guide such projects and encourage circular economy practices locally and globally.
Future Trends and Opportunities
Advanced Recycling Technologies
Innovations like chemical recycling and waste-to-materials processes will enable the recovery of valuable resources from more types of waste materials. The goal is to conserve and reduce the need for new materials.
Decentralized Waste Management
Small-scale anaerobic digesters and on-site composting facilities can turn organic waste into energy and valuable soil amendments. These systems help reduce the strain on centralized waste treatment facilities and transportation networks, being easy to implement and maintain. Plus, they align with sustainability goals, enhance resource recovery, and offer opportunities for individuals, small businesses, and communities to participate in green initiatives.
Circular Economy Business Models
More businesses recognize the value of reducing waste, reusing materials, and implementing self-sufficient waste management solutions. This shift towards circularity minimizes a company’s environmental footprint and can create new revenue streams. Moreover, businesses that embrace circular principles are more likely to meet consumer demands for eco-friendly products and services while contributing to sustainability goals.
FAQs:
Can waste be transformed into energy?
Yes, you can turn waste into energy through incineration, anaerobic digestion, gasification, and pyrolysis, among other processes. WTE technology can convert trash into green electricity, heat, or biogas, contributing to an efficient waste management system and reducing landfill volumes.
What is waste energy called?
Waste can generate several forms of energy, including electricity, heat, biogas, and biofuels. The specific type of energy generated depends on the waste composition and the chosen waste-to-energy process. Waste energy is considered green energy due to its potential to reduce environmental harm. However, whether it’s classified as renewable depends on the waste composition.
What are the cons of converting waste into energy?
Some waste-to-energy processes generate pollutants and greenhouse gases, which concern the environment. Additionally, using municipal waste as an energy source might discourage efforts to reduce and recycle waste. From an economic perspective, building and operating waste-to-energy plants can be expensive. Furthermore, getting these plants approved in communities is challenging because residents often raise concerns about air quality, noise, and perceived health risks.
What are the benefits of turning waste into energy?
The process has multiple benefits. It helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, conserving valuable space, reducing water and soil pollution risks, and minimizing methane and carbon emissions. By generating green electricity and heat, it helps to stabilize energy grids and promotes responsible waste management practices and can be economically viable, creating jobs and supporting local, circular economies.
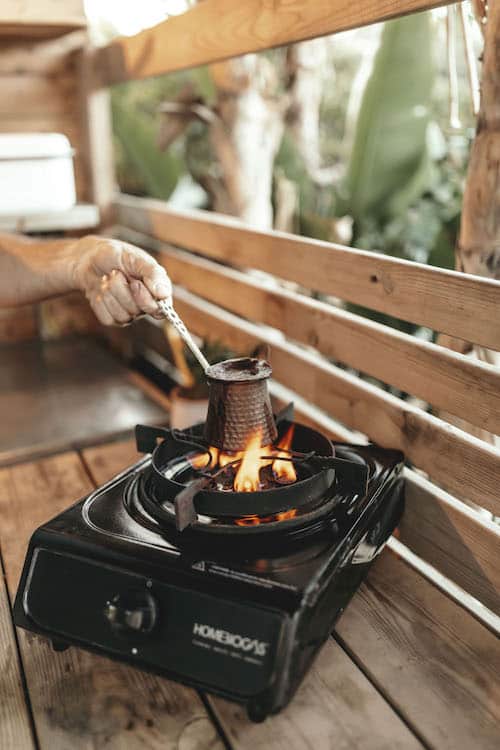
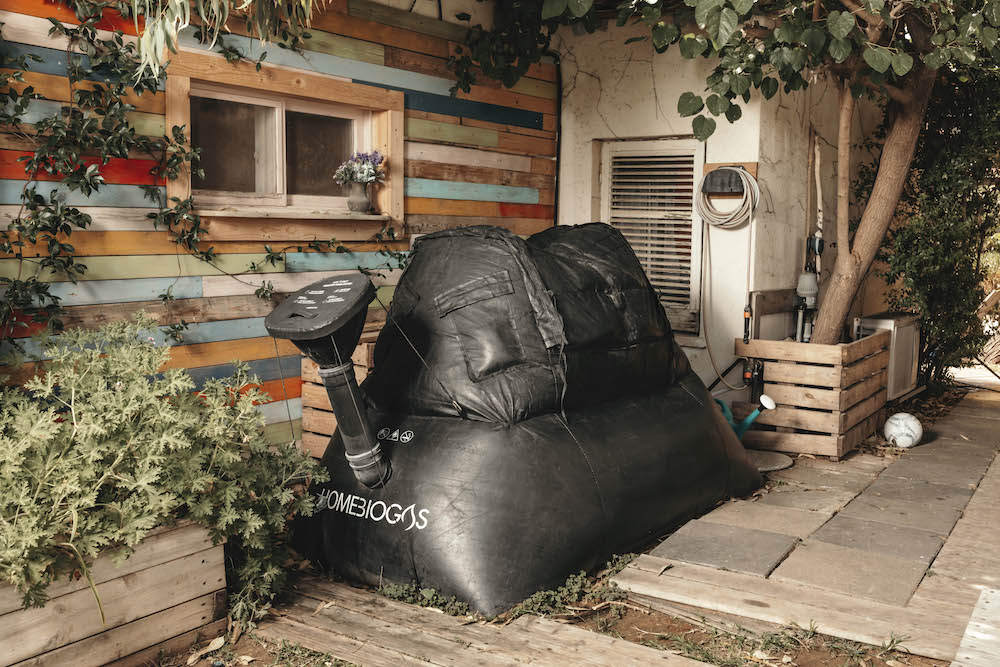
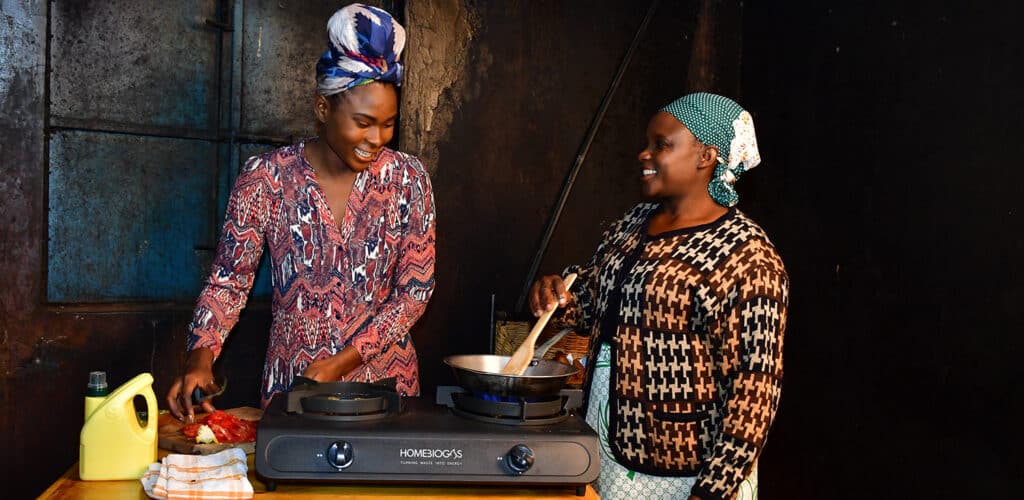
Meet HomeBiogas — Turn your organic waste into clean energy
HomeBiogas systems encourage a transformative approach to waste-to-energy, helping individual households and small businesses to actively contribute to sustainability goals.
A HomeBiogas system includes an anaerobic digester (a biodigester), dedicated gas pipes, and a specially designed burner, making organic waste management easy and accessible for homeowners.
The biodigester can process organic kitchen waste and livestock manure to generate biogas for cooking. The convenience of turning food waste into energy on-site reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering carbon emissions and energy costs. Beyond producing biogas, the residual byproduct of the process (digestate) is a valuable organic fertilizer. This nutrient-rich material can be applied to gardens and farms, enhancing soil health and fertility.
With multiple system sizes available, from compact options suitable for small families to larger models catering to extensive domestic needs, HomeBiogas accommodates many households, small farms, and businesses.
The Takeaway
Transforming waste into energy isn’t just a possibility; it’s crucial to sustainable waste management and generating green and renewable energy. With diverse WTE technologies and strategies, individuals and communities can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while repurposing waste as a valuable source for clean energy production.
Embracing responsible waste management practices enables everyone to play an active role in shaping a greener future. Whether you’re looking for user-friendly home systems or supporting large-scale community efforts, there’s a suitable solution for anyone who aims to participate in this transformative journey.